July 07, 2020
What are perforator flaps? How are they used in breast reconstruction?
Microsurgical breast reconstruction using perforator flaps represents the state of the art in reconstructive breast surgery after mastectomy. The tissue removed by the mastectomy is replaced with the patient’s own living tissue to recreate a “natural”, warm, soft breast which is permanent and unlike implants, can never leak or rupture.
Skin, fatty tissue, and the tiny blood vessels (“perforators”) that supply nutrients to the tissue can be taken from the patient’s abdomen (SIEA flap and DIEP flap procedures), and buttocks (GAP flap). Unlike conventional tissue reconstruction techniques (like the TRAM flap), these perforator flap techniques carefully preserve the patient’s underlying musculature. The tissue is then transplanted to the patient’s chest and reconnected using microsurgery.
Preserving underlying muscles lessens postoperative discomfort making the recovery easier and shorter, and also enables the patient to maintain muscle strength long-term. This is particularly important for active women.
While microsurgical breast reconstruction offers many advantages to the patient, the surgeries are very complex and time-consuming and specialized training is required. Before choosing a surgeon ensure that he/she is a plastic surgeon certified by the American Board of Plastic Surgery and has extensive experience with perforator flap breast reconstruction. Ask about the success rate of the procedure in their hands (most specialists boast a flap survival rate of at least 97%) and how many they have performed.
Insurance companies are federally mandated to pay for the cost of breast reconstruction. Unfortunately, some patients will still face difficulties in gaining access to perforator flap specialists. Here again it pays to seek out plastic surgeons who specialize in DIEP flap, SIEA flap and GAP flap breast reconstruction as typically an insurance specialist is available to help patients with insurance issues.
Our surgeons perform over 700 microsurgical breast procedures with perforator flaps per year (with a success rate of 99%+) making PRMA Plastic Surgery one of the busiest and most successful breast reconstruction centers in and beyond the USA.
To learn more about each of the perforator flap techniques offered at PRMA please click on the relevant link:
To learn if you are a candidate for breast reconstruction using your own tissue, or to schedule a consultation, please contact us here or call us on (800) 692-5565.
Author: Dr. Minas Chrysopoulo
Microsurgical breast reconstruction using perforator flaps represents the state of the art in reconstructive breast surgery after mastectomy. The tissue removed by the mastectomy is replaced with the patient’s own living tissue to recreate a “natural”, warm, soft breast which is permanent and unlike implants, can never leak or rupture.
Leave Comment
Sign Up for Our Monthly Newsletter
Continue Reading

How To Choose A Breast Reconstruction Plastic Surgeon That Is Right For You
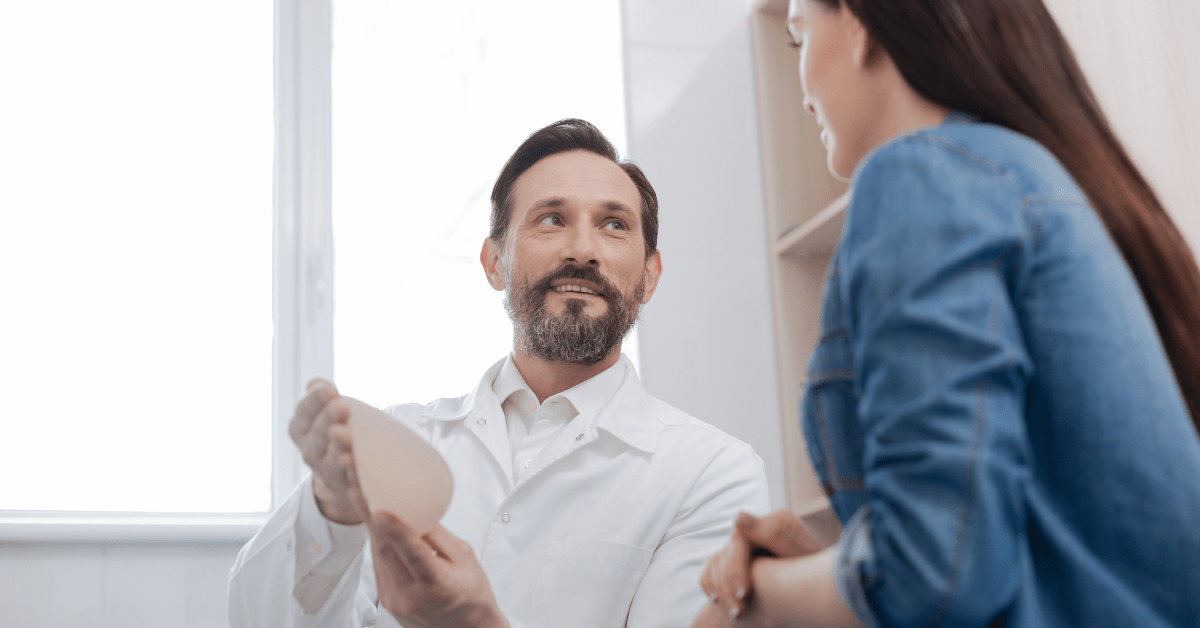
How To Choose A Breast Reconstruction Plastic Surgeon That Is Right For You April 07, 2021 Share on Facebook Twitter Linkedin When considering and planning for breast reconstruction, it is important to find the right surgeon for you. Identifying a surgeon who is board-certified in plastic surgery should always be the first step. You can […]

3D Nipple-Areola Tattooing After Breast Reconstruction: Here’s What You Need to Know
3D Nipple-Areola Tattooing After Breast Reconstruction: Here’s What You Need to Know March 31, 2021 Share on Facebook Twitter Linkedin One of the several options patients have after breast reconstruction surgery is complete, is to have the appearance of the nipple and areola recreated with a tattoo. These tattoos are applied using needles that insert […]
Who Needs Breast Reconstruction Surgery?
Who Needs a Breast Reconstruction Surgery? March 17, 2021 Share on Facebook Twitter Linkedin Patients who have lost their breast(s), are planning to remove their breast(s) tissue to reduce their risk of breast cancer, who have significant asymmetry due to a lumpectomy or a mastectomy, or even a botched reconstructive surgery from another facility are […]

Lymphedema Surgery: Why PRMA Plastic Surgery Does It Better
Lymphedema Surgery: Why PRMA Plastic Surgery Does It Better March 10, 2021 Share on Facebook Twitter Linkedin Lymphedema, or arm swelling, is a known potential complication after breast cancer surgery. The swelling is caused by a build up of fluid caused by inadequate lymphatic drainage. It can happen after any surgery involving the lymph nodes […]

Mastectomy Reconstruction: Here’s What You Need to Know
Mastectomy Reconstruction: Here’s What You Need to Know March 03, 2021 Share on Facebook Twitter Linkedin Mastectomy reconstruction, or breast reconstruction, can take place at the same time as a mastectomy. Likewise, reconstruction can take place anytime after breast cancer surgery. When the reconstruction surgery is performed at the time of mastectomy, it is referred […]

What is Recovery Like After Breast Reconstruction?
What is Recovery Like After Breast Reconstruction? February 17, 2021 Share on Facebook Twitter Linkedin Healing after surgery is a process and many of our patients always want to know what recovery is like after breast reconstruction. Our first response is always to remind patients the healing journey is not linear. Everyone is different. However, […]

PRMA Performs Record Breaking 9500th Flap-Based Breast Reconstruction Procedure
PRMA Performs Record Breaking 9500th Flap-Based Breast Reconstruction Procedure February 03, 2021 Share on Facebook Twitter Linkedin The team at PRMA Plastic Surgery | Center for Advanced Breast Reconstruction in San Antonio, Texas has set a new practice record after completing their 9,500th free-flap breast reconstruction procedure. Free-flap breast reconstruction is today’s most advanced breast […]
PRMA Surgeons Share Their COVID-19 Vaccine Experiences
PRMA Surgeons Share Their COVID-19 Vaccine Experiences February 03, 2021 Share on Facebook Twitter Linkedin Currently, the state of Texas is administering COIVD-19 vaccines to healthcare workers and individuals 65 and older, or those who have underlying health conditions that increase their risk for sever COVID symptoms. To do our part in the fight against […]

Are Tissue Expanders Necessary Before DIEP Flap Breast Reconstruction?
Are Tissue Expanders Necessary Before DIEP Flap Breast Reconstruction? January 28, 2021 Share on Facebook Twitter Linkedin Breast reconstruction is not a cookie-cutter procedure. Typically, reconstruction is done in stages for optimal cosmetic outcomes. What happens during each phase can look very different from one individual to another. A question we receive often is, “Are […]

Will My Nipples Have Feeling After a Mastectomy and Breast Reconstruction?
Will My Nipples Have Feeling After a Mastectomy and Breast Reconstruction? January 21, 2021 Share on Facebook Twitter Linkedin For many women facing a mastectomy, the possibility of losing their nipple may come as a surprise. For some patients, a procedure that saves the nipple and areola, known as a nipple-sparing mastectomy, may be an […]

No Comments